One of our readers posted a question on forum asking how to get weather data using VBA. So I created a very simple weather app in Excel VBA. It looks like gif below
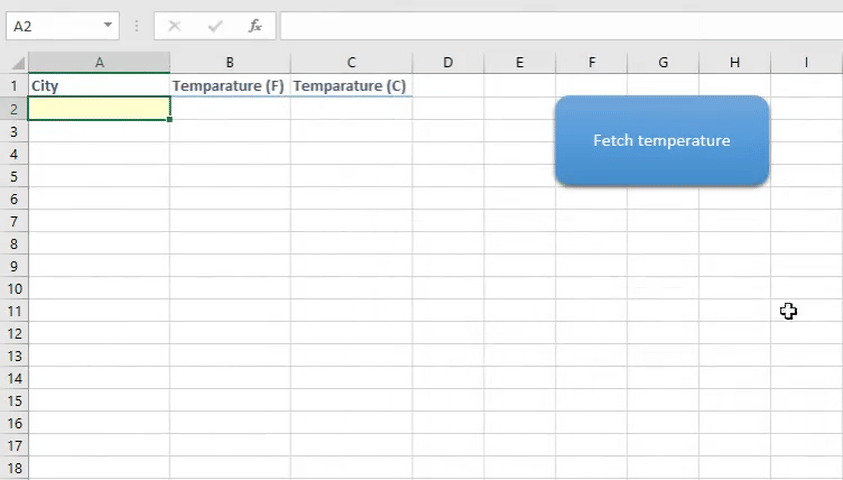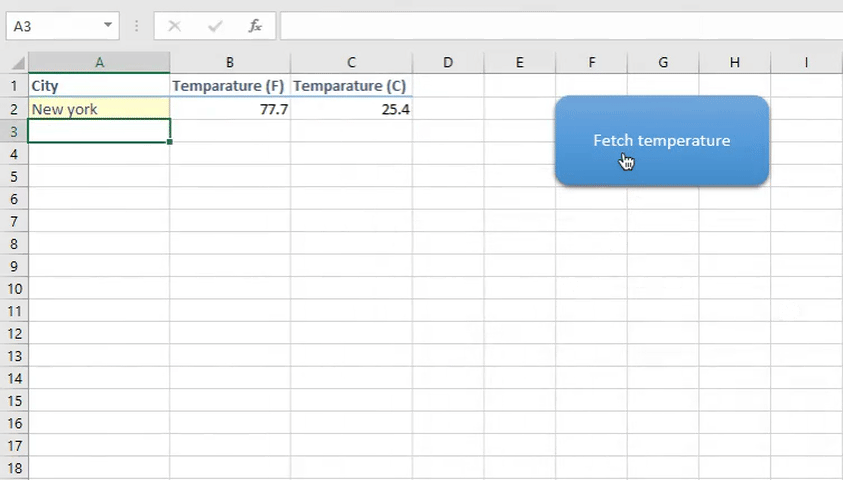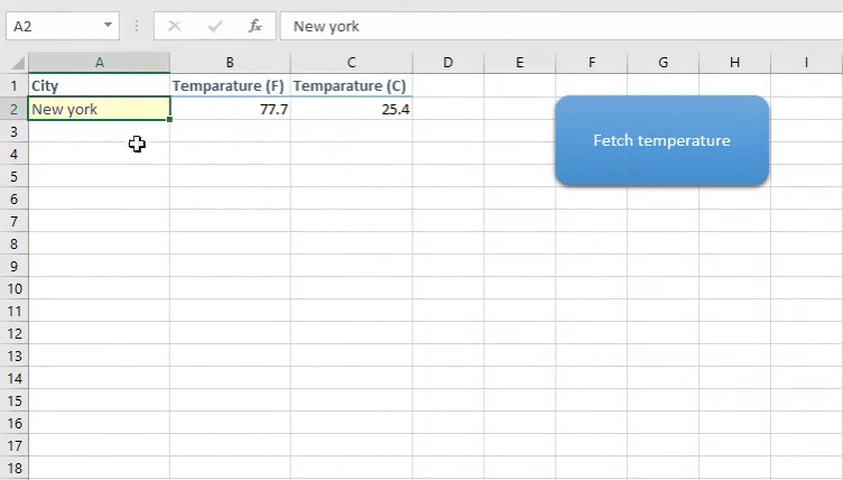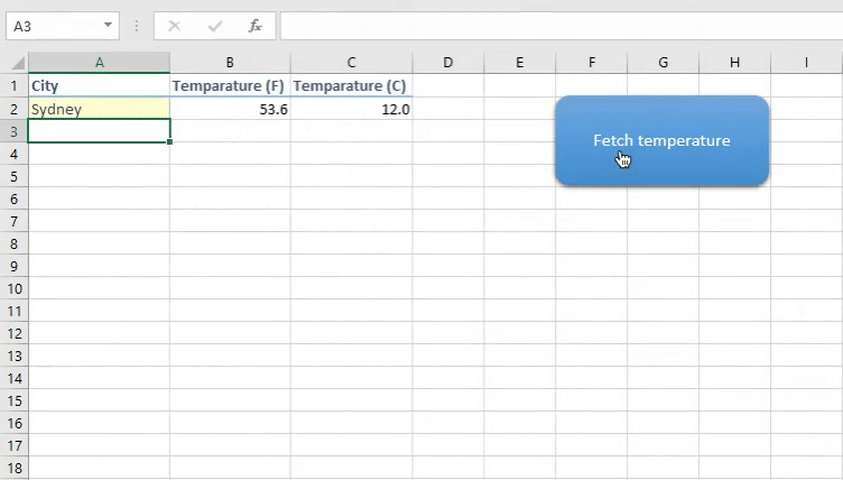
Understanding weather API
I’m using a free weather API from https://openweathermap.org/ to fetch the weather data for a city. Don’t get scared When I say API. It’s a simple URL which has to be called with few parameters and it returns the weather data in JSON, XML or HTML format.
Try copy pasting this URL into your browser
http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?apikey=4a2360d14bf33378079d2e2d49e35ddb&mode=xml&units=imperial&q=newyork
It returns response like this

Look at the URL parameters mode=xml, units=imperial, apikey=YourAPIKey and q=newyork. Parameter name says it all. VBA supports XML built-in so I used mode=xml to return data in XML format.
Imperial units for getting the temperature in Fahrenheit, q parameter for the city name and API key for authentication. Read complete documentation of the API here – Weather API Documentation
I’ve given my API key here but use your own API key by signing up – Openweathermap API key. It’s FREE mate!
Using weather API in VBA
So all we have to do is call the API and parse the response to get weather data for a city. Have a look at the code once
Public Sub getWeather()
Dim xmlhttp As New MSXML2.xmlhttp, myurl As String, xmlresponse As New DOMDocument
myurl = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?apikey=4a2360d14bf33378079d2e2d49e35ddb&mode=xml&units=imperial&q=" & Sheets(1).Range("A2").Value
xmlhttp.Open "GET", myurl, False
xmlhttp.Send
xmlresponse.LoadXML (xmlhttp.responseText)
Sheets(1).Range("B2").Value = xmlresponse.SelectNodes("//current/temperature/@value")(0).Text
'MsgBox (xmlresponse.getElementsByTagName("temperature")(0).Attributes(1).Text) Alternate method to parse XML
End Sub
Code explanation
- First, we make a simple GET request to weather API with city name which is pulled from cell A2 in sheet 1. Read about HTTP requests in VBA here
- Define a DOM document and load API response into that document using loadXML method.
-
Finally we parse the temperature data using XPath or any other method.
SelectNodesmethod can be used to select an element by passing XPath. There are different ways to parse XML. I’ve mentioned 2 methods in the above code. Read the official documentation for Dom document VBA to experiment with different methods
How to use code (For VBA beginners)
Press Alt + F11 in Excel to open VBA code editor then insert a new module and paste the above code. Also, Don’t forget to add a reference to Microsoft XML object to parse XML response. Do it in this way – Tools > references – Microsoft XML X.0 > select and click ok.
Now run the code using F5 or play button in the code editor. If you want to run the code from Excel using a button as shown in the gif above then insert a shape from Insert tab > right click on the shape and assign macro.
Understanding XPath
I’ve used this XPath – //current/temperature/@value which means open element with tag current, then open element with tag temperature and then get the value of attribute named value Read more about XPath selectors here – List of all XPath selectors
Wrapping up
JSON API can also be used if you are not a fan of XML. Read how to Parse JSON in VBA here and give it a try!
If you have and questions or feedback, comment below.
- Ultimate Guide: Build A Mobile E-commerce App With React Native And Medusa.js - February 15, 2025
- Flutter lookup failed in @fields error (solved) - July 14, 2023
- Free open source alternative to Notion along with AI - July 13, 2023
Is there a MAC OS equivalent to the httprequest available in Excel?
Slight modification with newer versions of Excel:
in Tools -> References, check off MS XML, v6.0
in the second line, MSXML2.xmlhttp needs to be changed to MSXML2.XMLHTTP60
also in the second line, DOMDocument needs to be changed to MSXML2.DOMDocument60
Can you please take a look at my code? It still doesn’t work…
Public Sub getWeather()
Dim xmlhttp As New MSXML2.XMLHTTP60, myurl As String, xmlresponse As New MSXML2.DOMDocument60
myurl = “http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?apikey=4a2360d14bf33378079d2e2d49e35ddb&mode=xml&units=imperial&q=” & Sheets(1).Range(“A2”).Value
xmlhttp.Open “GET”, myurl, False
xmlhttp.Send
xmlresponse.LoadXML (xmlhttp.responseText)
Sheets(1).Range(“B2”).Value = xmlresponse.SelectNodes(“//current/temperature/@value”)(0).Text
‘MsgBox (xmlresponse.getElementsByTagName(“temperature”)(0).Attributes(1).Text) Alternate method to parse XML
End Sub
This is pretty neat but isn’t functional as is. Just an FYI for anyone who has come across this page
This works:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim xmlhttp As Object
Dim myurl As String
Dim xmlresponse As Object
Set xmlhttp = CreateObject(“MSXML2.serverXMLHTTP”)
Set xmlresponse = CreateObject(“MSXML2.DOMDocument”)
myurl = “http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?apikey=4a2360d14bf33378079d2e2d49e35ddb&mode=xml&units=imperial&q=” & Tabelle15.Range(“A2”).Value
xmlhttp.Open “GET”, myurl, False
xmlhttp.Send
xmlresponse.LoadXML (xmlhttp.responseText)
Tabelle15.Range(“B2”).Value = xmlresponse.SelectNodes(“//current/temperature/@value”)(0).Text
‘MsgBox (xmlresponse.getElementsByTagName(“temperature”)(0).Attributes(1).Text) Alternate method to parse XML
End Sub